Identify the Level of Protein Structure Matching Each Description.
This is also known as the sequence of the protein. What forms the secondary level of protein.
The sequence of amino acids Choose.
. Students should be able to identify the four levels of protein structure and the molecular forces or interactions responsible for stabilizing each level of structure. Secondary The formation of a protein is created using a hierarchy of structures. By convention four levels of protein organization may be identified.
Chemistry questions and answers. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structure. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary.
Identify each of the levels of protein structure in the diagrams. Match the organelle with its function 1. 2 There may be several answers for some of these.
Primary structure Tertiary structure Secondary. Biochemists talk about protein structure at four distinct levels. 100 Identify the level of protein structure matching each description.
Give the name and description of the first level of protein structure. Not yet answered Points possible. Primary Structure This is the sequence of amino acids joined together by strong covalent peptide bonds.
The primary structure of a peptide or protein is the linear sequence of its amino acids AAs. Orders of protein structure. This native state can be disrupted by.
Hydrogen bonds are formed between certain amino acids. Each peptide bond is broken and products are all of the free amino acids. Levels of Protein Structure.
1 The protein to consider here is collagen. Match each description to its correct level of protein structure Alpha helix. Chaperones bind to protein as it enters the matrix.
Alpha helix and beta pleated sheet. 100 Identify the level of protein structure matching each description Small 3D features determined by hydrogen bonding Choose. What characterizes the protein in the primary level.
Match Each Description With Correct Level of Protein Structure Match the protein to the descriptions. The sequence of amino acids Choose. - The three dimensional structure of a protein made of 1 polypeptide - Complexes of 2 3 4 etc protein molecules are called dimers trimers.
For simplicity a proteins structure can be depicted in several different ways each emphasizing different features of the protein. By convention the primary structure of a protein is read and written from the amino-terminal N to the carboxyl-terminal C end. 20 different amino acids are found in proteins.
Nucleus Contains instructions for protein synthesis and cell reproduction. Overall 3D shape of a protein Choose. Secondary Structure 2 -- Alpha Helices.
The hydrogen bonds frequently occur between back. Endoplasmic reticulum Intracellular compartment forms transport vesicles. Answer 1 of 2.
Matrix-targeting sequence binds to receptor. To explain the shape of proteins it is important to know the four levels of protein structure. For each image match the term and the written description of.
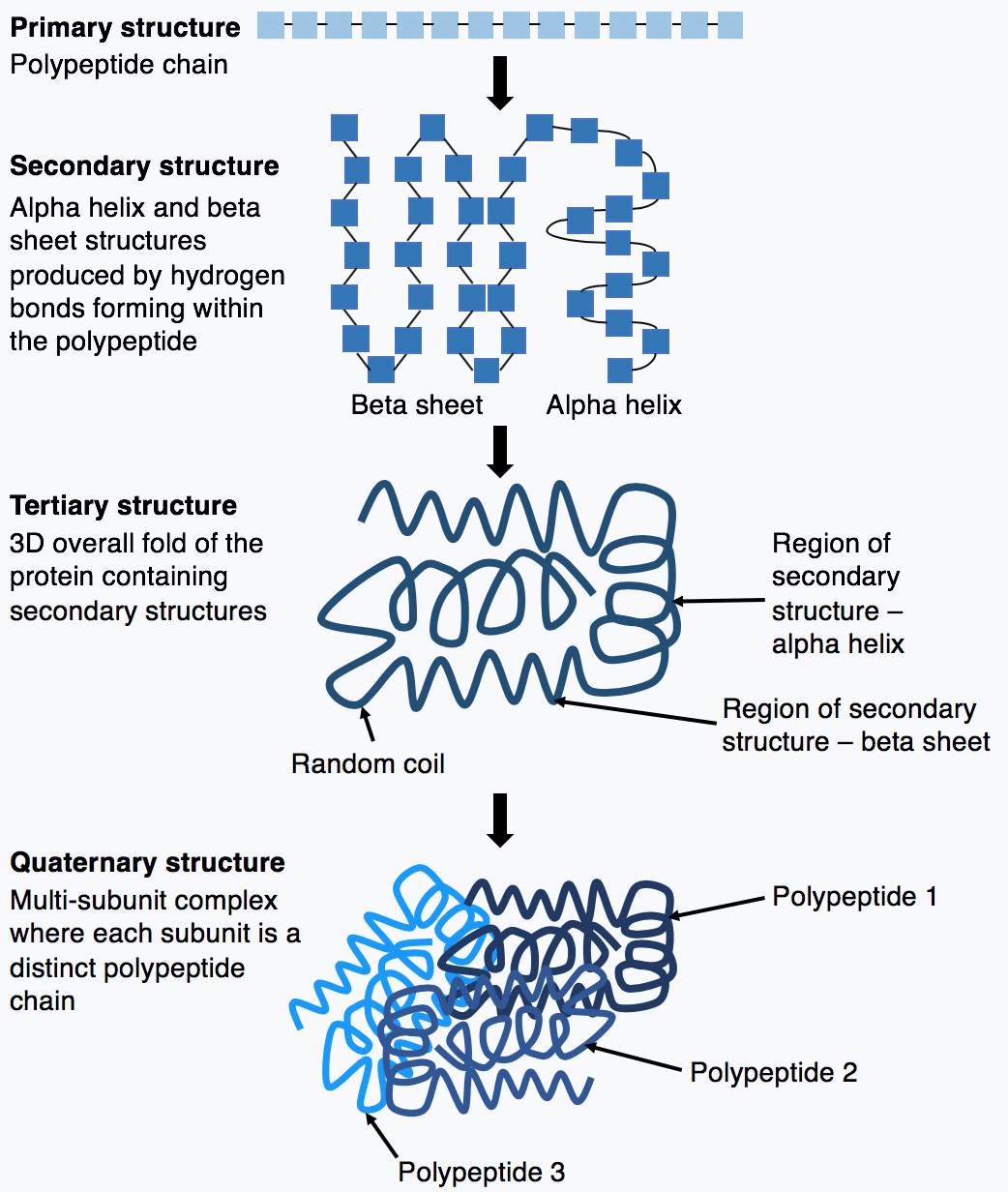
The primary structure of protein is the hierarchys basic level and is the particular linear sequence of amino acids comprising one polypeptide chain. The secondary structure consists of local packing of polypeptide chain into α-helices and β-sheets due to hydrogen bonds between peptide bond central carbon backbone. Proteins have four levels of organization.
Amino acid sequence C. -The number and type of amino acids present. Overall three-dimensional shape B.
The detailed structure of any protein is complicated. Choose from these descriptions. Each amino acid is separated identified and quantified.
Then choose the descriptions from the list below that go with each of the levels. Select all that apply. Orders of protein structure.
Major determinant of a proteins characteristics. Four levels of protein structure. Secondary structure is the next level up from the primary structure and is the regular folding of regions into specific structural patterns within one polypeptide chain.
Number and order of amino acids. Chaperones are released as protein is transferred to a channel in the outer membrane. No partial credit.
Overall 3D shape of a protein Tertiary structure Interaction of multiple of. Primary structure refers to the linear sequence of the amino acids connected by the peptide bonds. PRIMARY STRUCTURE 1.
Each amino acid is connected to the next by a peptide bond. Small 3D features determined by hydrogen bonding Choose. Protein is transferred to a channel in the inner membrane 5.
Features of the Primary Structure -The amino acids are joined together by strong covalent peptide bonds. Secondary structure - consists mostly of hydrogen bonds between local areas of a protein sequence. Participates in lipid synthesis and synthesis of membrane or secreted proteins.
Primary structure the linear sequence of amino acids held together by covalent. These are called the primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structures of the protein. The different levels of protein structure are known as primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structure.
Primary structure - consists of covalent peptide bonds between amino acids. Chaperone proteins keep proteins unfolded. Match each name with the appropriate structure in the diagram.
Not yet answered Points possible. Primary Structure of Proteins The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain. Martix-targeting sequence binds to receptor.
Below are depictions of each of these levels of protein structure. The term native state is used to describe the protein in its most stable natural conformation in situ. 138139 presents four different depictions of a protein domain called SH2 which has important functions in eucaryotic cells.
- Contains intrachain hydrogen bonds - Contains heptad repeats - Contains Glycine at every 3rd residue. Primary secondary tertiary quatrenary article Khan Academy. Consists of the linear amino acids joined together by peptide bonds.
Match each description to its correct level of protein structure Beta-pleated sheet. Biologists distinguish 4 levels of protein structure. Due to the nature of the weak interactions controlling the three-dimensional structure proteins are very sensitive molecules.
The four levels of protein structure are shown in Figure 2.
Match Each Description With The Correct Level Of Protein Structure At Level

Comments
Post a Comment